A Guide to Running Cron Jobs on Amazon Machine Image (AMI) using Crontab
In this blog post, we will explore how to run cron jobs on an AMI using the crontab utility, providing a step-by-step guide to help you automate your tasks efficiently.
, #_
~\_ ####_ Amazon Linux 2023
~~ \_#####\
~~ \###|
~~ \#/ ___ Running Cron Jobs on AMI
~~ V~' '->
~~~ /
~~._. _/
_/ _/
_/m/'
What is Cron and What does it do?
Cron is a time-based job scheduler in Unix-like operating systems that allows users to automate repetitive tasks. It is an essential tool for developers who want to schedule and execute commands or scripts at specific intervals.
Cron operates using a file called the "cron table" or "crontab." The cron table contains a list of commands or scripts along with their schedule, specifying when and how often they should be executed. These scheduled commands or scripts are known as "cron jobs."
First and foremost, let's try to understand the cron syntax
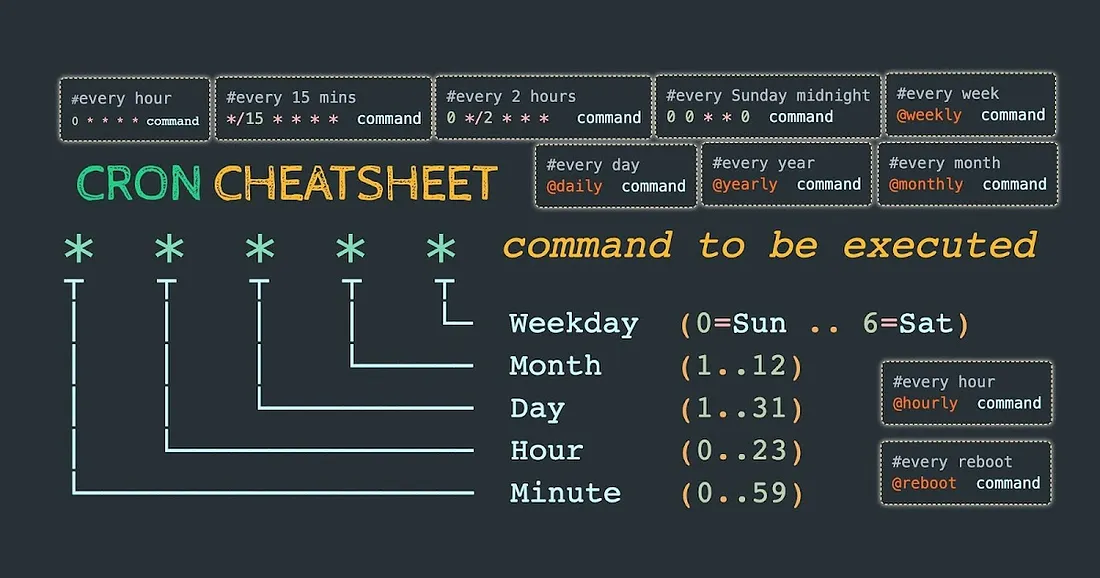
This is how a one-liner cron job looks like, It's essential to understand the cron syntax here, which consists of six fields:
* * * * * command_to_be_executed
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ └─── Day of the week (0 - 7, where both 0 and 7 represent Sunday)
│ │ │ └──────── Month (1 - 12)
│ │ └───────────── Day of the month (1 - 31)
│ └────────────────── Hour (0 - 23)
└─────────────────────── Minute (0 - 59)
Let's get started with the steps now.
Step 1: Accessing your AMI:
To begin, you need to access your AMI either through the AWS Management Console or by connecting to your instance via SSH.
Step 2: Installing crontab:
By default, crontab is not installed on some AMIs, so you may need to install it. To install crontab, execute the following command:
sudo yum install cronie
Step 3: Editing the cron table:
Once crontab is installed, you can edit the cron table by running the command:
crontab -e
This will open the cron table in your default editor. For example, to schedule a task to run every day at 2:30 AM, add the following line:
30 2 * * * command_to_be_executed
~
~
~
"/tmp/crontab.Jt72NEAVtu" 0L, 0B
That's it!! You have successfully learned the basics of crontab now, lets deep dive using an example now.
Learn by doing :)
We will look at some of the most common use cases of cron jobs. We will use an example where we will run a script every 3 hours using Crontab.
Let's create a simple script that will print the current time and date to a file called date.txt. To do this, create a file called date.sh and add the following lines:
#!/bin/bash
date >> date.txt
Save the file and make it executable by running the command:
chmod +x date.sh
Now, to schedule this script to run every 3 hours, open the cron table by running the command:
crontab -e
Add the following line to the cron table:
0 */3 * * * /path/to/date.sh
Save the file and exit the editor. This will schedule the script to run every 3 hours. And that's how you have created your first cron job on your AMI.
Few commands that will help you manage your cron jobs:
> Checking the status of cron jobs:
To check the status of cron jobs, run the command:
crontab -l
This will list all the cron jobs that are scheduled to run on your AMI.
> Deleting cron jobs:
To delete a cron job, run the command:
crontab -r
This will delete all the cron jobs that are scheduled to run on your AMI.
> Restarting cron service:
To restart the cron service, run the command:
sudo service crond restart
This will restart the cron service on your AMI.
> Checking the status of cron service:
To check the status of cron service, run the command:
sudo service crond status
This will display the status of cron service on your AMI.
> Checking the logs of cron jobs:
To check the logs of cron jobs, run the command:
sudo tail -f /var/log/cron
This will display the logs of cron jobs on your AMI. By default, cron job output is sent to the user's email address associated with the AMI. To check the output, you can use the mail command. For example:
mail
This will display any incoming mail, including the output of cron jobs.
Conclusion:
Automating tasks using cron jobs on an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) can greatly simplify your workflow and save you time. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily schedule and manage cron jobs on your AMI using the crontab utility. Remember to test and validate your cron jobs to ensure they are functioning as expected.
Thanks for reading, folks :)